In an extraordinary meteorological phenomenon, six cyclones are currently swirling simultaneously across the Southern Hemisphere, presenting both awe and concern for scientists and weather enthusiasts alike. This rare event, reported by The Guardian, underscores the dynamic nature of global weather systems and raises questions about the implications of such a convergence of storms. As these powerful atmospheric disturbances develop and interact, their impact on surrounding regions could be profound, affecting millions of lives and shaping weather patterns for weeks to come. This article delves into the details of each cyclone, examines their potential trajectories, and explores the broader climate trends contributing to this unusual occurrence in our ever-changing atmosphere.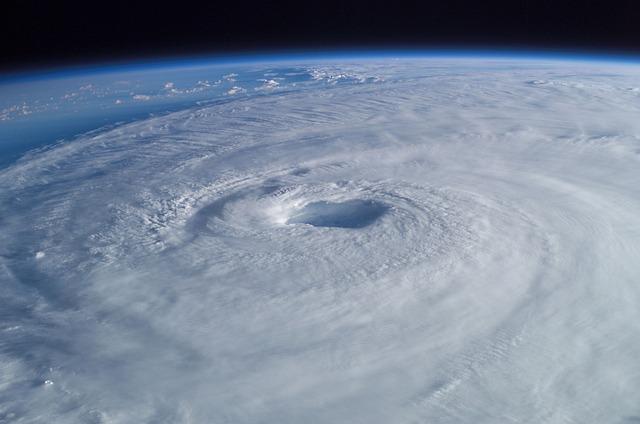
Impact of Concurrent Cyclones on Regional Weather Patterns
The simultaneous occurrence of six cyclones in the southern hemisphere has profound implications for regional weather patterns. As these powerful storm systems interact,their overlapping influences can exacerbate localized weather phenomena,leading to unpredictable outcomes.Observers note the potential for increased precipitation, dramatic shifts in temperature, and heightened wind speeds, all of wich can affect communities, agriculture, and ecosystems alike.The unique combination of these cyclonic forces may create a scenario where areas that are typically sheltered from severe weather could face unprecedented turmoil.
Moreover, the interaction between cyclones can produce complex atmospheric behaviors, resulting in phenomena such as storm surges, turbulent airflows, and enhanced moisture transport across vast distances. The table below outlines key factors to consider when assessing the effects of concurrent cyclones on regional climates:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Wind Patterns | Increased disruption and potential for destructive gusts |
| Precipitation Levels | Significant rainfall increases resulting in flooding |
| Temperature Fluctuations | Possible abrupt changes affecting local climates |
| Cyclone Paths | Altered trajectories leading to unexpected landfalls |
Along with immediate weather impacts, the long-term effects of multiple cyclones can reshape the climate resilience of affected regions. Communities must adapt to increased vulnerability as past weather patterns may no longer serve as reliable indicators for future events. This necessitates a comprehensive approach to disaster preparedness, with an emphasis on understanding the shifting dynamics of storm behavior as the climate continues to evolve.

Understanding the Formation and Development of Southern Hemisphere Cyclones
The formation of cyclones in the Southern Hemisphere is a complex interplay of meteorological factors. These powerful storms typically develop over warm ocean waters, which provide the necessary heat and moisture. In particular, the Saffir-Simpson scale helps categorize cyclones based on wind speeds and resulting potential damage.A cyclone begins to form when the sea surface temperature rises above 26 degrees Celsius,coupled with atmospheric instability and low vertical wind shear. These conditions allow warm, moist air to rise, creating a low-pressure area that attracts more air and amplifies the cyclone’s intensity.
As a cyclone intensifies,various structural features emerge. The eye, a calm region, is surrounded by the eyewall, where the most severe weather occurs. During this stage, the cyclone becomes classified into different categories, from tropical depressions to full-fledged hurricanes. Below is a simplified depiction of the different storm categories based on wind speeds:
| Category | Wind Speed (km/h) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 119-153 | Vrey risky winds will cause some damage. |
| 2 | 154-177 | Extremely dangerous winds will cause extensive damage. |
| 3 | 178-208 | Devastating damage will occur. |
| 4 | 209-251 | Catastrophic damage will occur. |
| 5 | 252+ | Catastrophic damage and severe impact on communities. |

Emergency Preparedness: Key Recommendations for Affected Communities
Communities in the path of simultaneously approaching cyclones must prioritize proactive measures to mitigate potential impacts. Establishing interaction channels is essential for relay of timely details regarding weather updates,evacuation plans,and safety protocols. To enhance community resilience, individuals should consider the following recommendations:
- Develop an Emergency Plan: Outline specific actions for various scenarios, including evacuation routes and designated meeting points.
- Create a Supply Kit: Gather essential supplies such as non-perishable food, water, medications, flashlights, and batteries to sustain yourself for several days.
- Stay Informed: Regularly monitor local news and weather reports for updates on cyclone developments and safety measures.
- Engage with Local Authorities: Attend community meetings to discuss preparedness strategies and resources available for residents.
Implementing community-wide preparedness drills can also foster cooperation among residents and local agencies. Utilizing resources such as social media platforms can further enhance real-time communication and alert systems. Below is a simple outline of community preparedness interests:
| Interest Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Community Meetings | Discuss collective responsibilities and develop preparedness strategies. |
| Resource Sharing | Pooling resources and support for affected households or individuals. |
| First aid Training | Empowering community members with essential emergency response skills. |
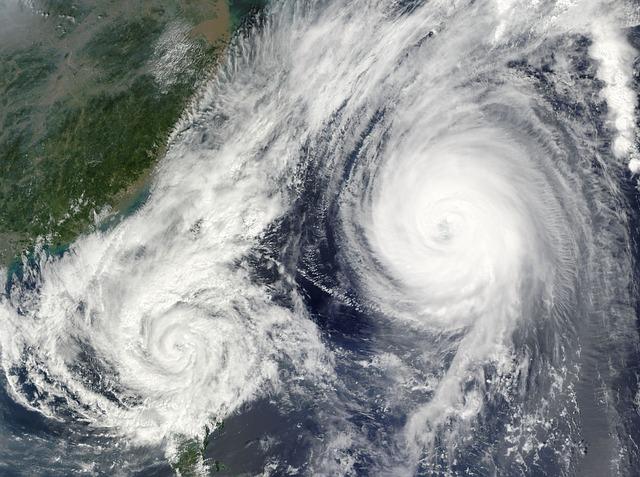

Global Implications: How These Storms Affect Climate Trends and Research
The simultaneous occurrence of multiple cyclones in the southern hemisphere not only captures the attention of meteorologists but also raises significant questions regarding global climate patterns. These extreme weather events serve as vivid indicators of shifting climate dynamics, contributing to a deeper understanding of long-term trends.Researchers are beginning to notice connections between intensified storm systems and factors such as:
- Rising sea surface temperatures that fuel cyclone strength
- Changes in atmospheric circulation impacting storm pathways
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events tied to climate change
Furthermore, the implications of these simultaneous cyclones extend beyond immediate weather forecasts. They act as a catalyst for ongoing climate research, prompting scientists to refine predictive models and enhance data collection practices. The table below summarizes recent findings related to cyclone activity and it’s potential correlation with climate anomalies:
| Cyclone Name | Date Formed | Maximum Wind Speed (km/h) | Area of Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclone A | 2023-07-01 | 220 | Southeast Coast |
| Cyclone B | 2023-07-02 | 185 | Pacific Islands |
| Cyclone C | 2023-07-03 | 200 | Southwestern Ocean |
| Cyclone D | 2023-07-04 | 240 | Western Australia |
The Way forward
As we conclude our exploration of the unprecedented weather events currently unfolding in the southern hemisphere,it is clear that the simultaneous formation of six cyclones presents both immediate challenges and long-term implications for affected regions. Meteorologists are closely monitoring these systems, emphasizing the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of increasingly erratic weather patterns exacerbated by climate change. As communities brace for impact, ongoing research and dialog will be crucial in developing effective response strategies and understanding the evolving dynamics of our planet’s climate. Stay informed, stay safe, and continue to follow updates as the situation progresses.