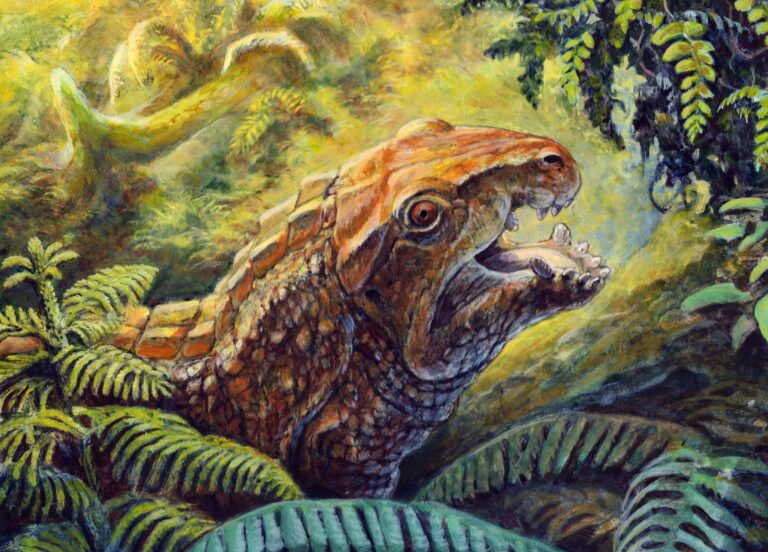
In a groundbreaking revelation that sheds light on prehistoric biodiversity, researchers have unveiled a new species of Triassic archosauriform in Brazil, a finding that could reshape our understanding of the evolutionary trajectory of this ancient group. Archosauriforms,the precursors to modern birds and crocodilians,roamed the Earth during a critical period of evolutionary history,offering insights into the diversification of reptiles following the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The newly identified species, which exhibits unique anatomical features not previously documented in the fossil record, provides valuable evidence of the ecological dynamics and adaptative strategies of these early terrestrial vertebrates. This discovery, detailed in a recent publication, underscores Brazil’s rich paleontological heritage and highlights the ongoing importance of fossil research in unraveling the complexities of life on Earth millions of years ago.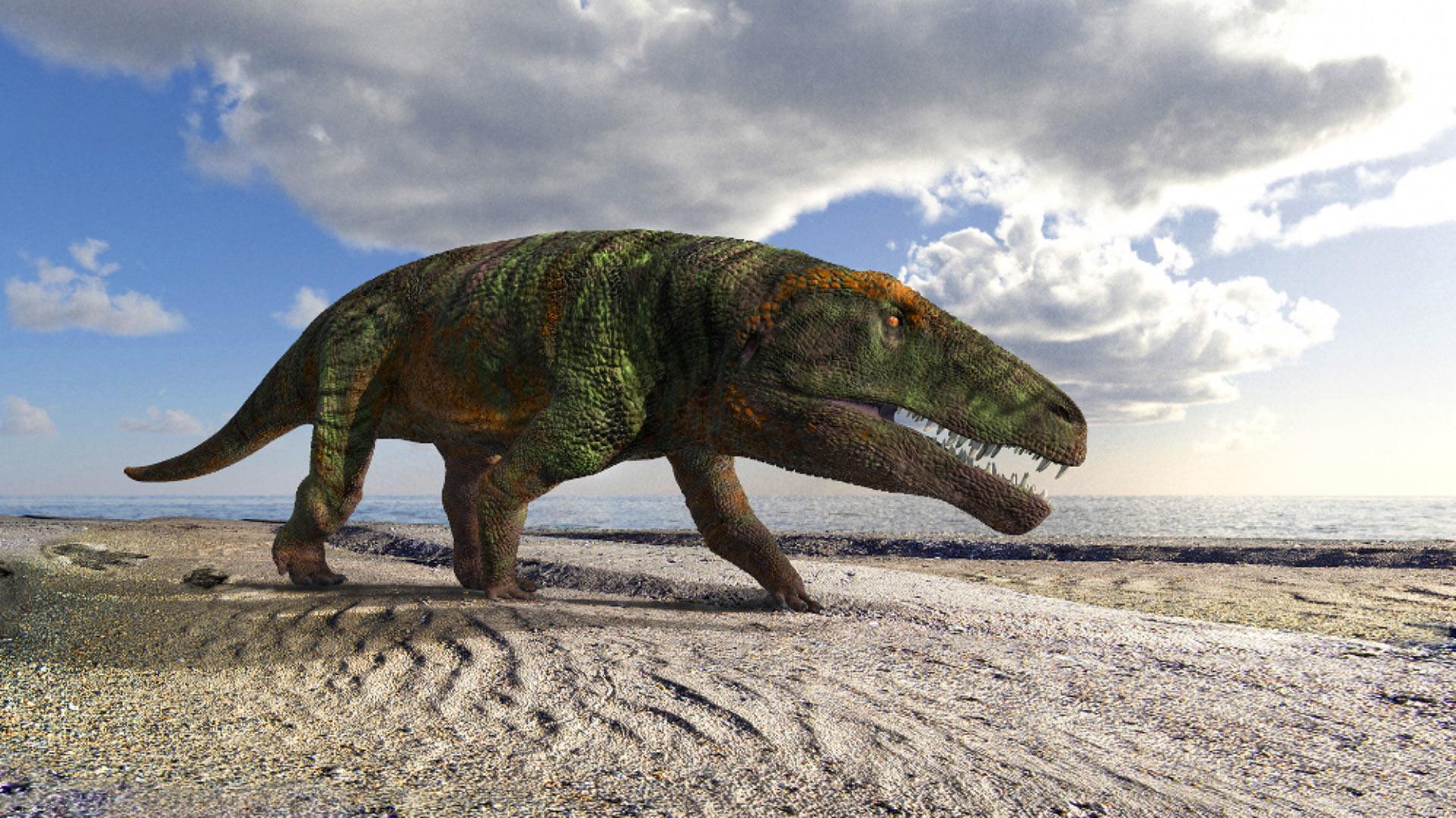
Discovery of a New Triassic Archosauriform: Unveiling Brazils Ancient Biodiversity
The recent discovery of a new Triassic archosauriform in Brazil has shed light on the rich tapestry of ancient biodiversity that once flourished on the supercontinent Gondwana. This remarkable find showcases a variety of unique characteristics that distinguish it from previously known species, providing invaluable insights into the evolutionary path of archosaurs. Key features include:
- Distinct skull morphology that suggests a specialized predatory lifestyle.
- Robust limb structure indicating adaptations for both terrestrial locomotion and possibly arboreal activities.
- Unique dental arrangement suitable for a varied diet, hinting at ecological versatility.
Fossil evidence indicates that this creature occupied a pivotal ecological niche, suggesting complex food webs in triassic ecosystems. Ongoing studies aim to unravel it’s precise relationship within the archosaur lineage, as comparisons are made with other meaningful finds from the same era. To contextualize this discovery within the broader narrative of prehistoric life, the table below illustrates some of the vital Triassic archosauriforms:
| Species | location | Era |
|---|---|---|
| Newly Discovered Species | Brazil | Triassic |
| Postosuchus | North America | Late Triassic |
| Stagonosuchus | Africa | late triassic |
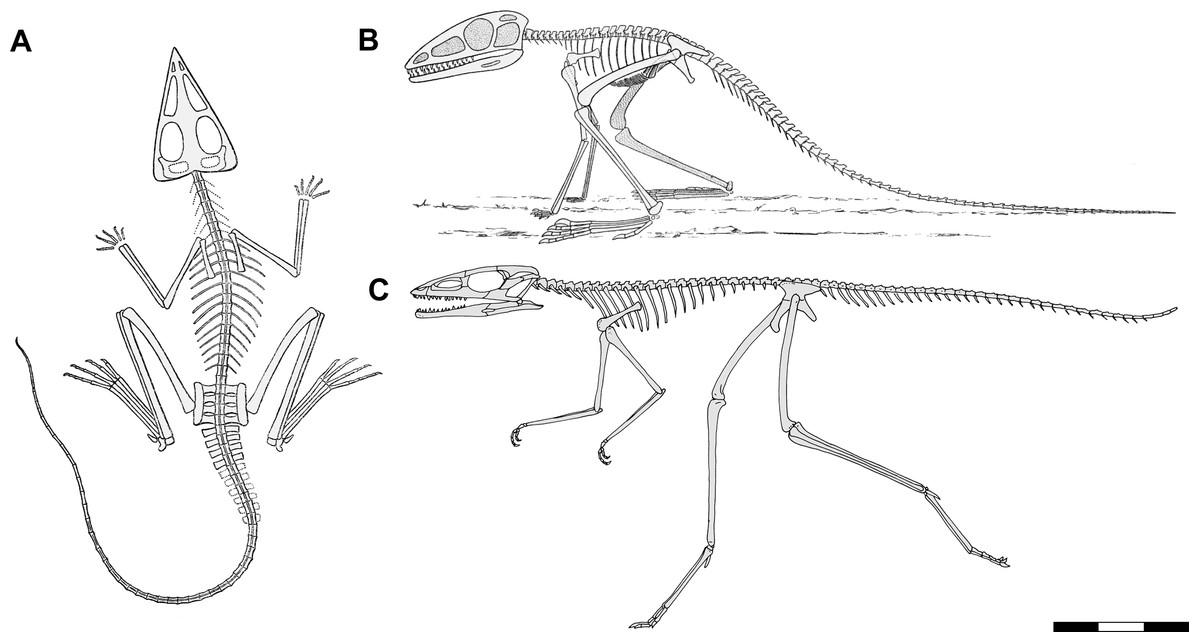
Anatomical Insights and Evolutionary Significance of the Newly Identified species
The discovery of this newly identified species of Triassic archosauriform in Brazil provides groundbreaking insights into the anatomical diversity of early archosaurs. Characterized by its distinct features,this species exhibits a combination of primitive and derived traits that highlight its unique evolutionary lineage. Notably, the skeletal structure displays:
- Robust limb bones: Suggesting a potentially agile lifestyle.
- Elongated vertebrae: Indicating advanced adaptations for dynamic movements.
- Unique cranial features: Reflecting diverse feeding strategies among contemporaneous species.
This species underscores the evolutionary significance of archosauriforms during the Triassic period, showcasing their adaptability in varying ecological niches. By analyzing the anatomical features in conjunction with existing phylogenetic data, researchers can trace pathways of evolutionary change, revealing how early archosaurs evolved to dominate terrestrial ecosystems. Moreover, such discoveries contribute to our understanding of the broader evolutionary themes observed during a time of profound change:
| Feature | Implication |
|---|---|
| Expanded nasal cavities | Possible enhanced respiratory efficiency. |
| Hind limb adaptations | increased locomotor capabilities. |
| Complex dentition | Diverse dietary habits. |
Implications for Triassic Ecosystems: Understanding the Role of Archosauriforms
The discovery of a new species of Triassic archosauriforms in Brazil sheds light on the intricate ecosystems of the period, which were marked by a shift in dominance from synapsids to these early archosaurs. With their emergence, archosauriforms likely played a crucial role in shaping the biodiversity of their habitats, influencing both flora and fauna. This discovery emphasizes the importance of archosauriforms as pivotal organisms that contributed to the ecological balance of Triassic environments, with potential impacts on:
- Predatory Dynamics: the rise of advanced archosauriforms would have introduced new predation strategies, altering food webs.
- Competition with Other Vertebrates: Their diverse adaptations may have led to increased competition with contemporary species, fostering evolutionary innovation.
- Habitat structuring: As they thrived in various niches, archosauriforms likely influenced the physical makeup of their ecosystems, affecting plant distributions and above-ground biomass.
Moreover,understanding the role of these archosauriforms provides insight into the post-triassic evolutionary trajectory that paved the way for dinosaurs.Analyzing the interactions between different species, including these newly discovered archosauriforms, can reveal patterns of adaptive radiation and environmental responses. The following table summarizes key characteristics of the newly identified species and their potential ecological roles:
| Species | Key Features | Potential Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| New Archosauriform | Medium-sized, bipedal, robust jaw structure | Top predator capable of influencing prey populations |
| Competitor Species | Slender, agile, specialized in foraging | Resource competitor impacting food availability |

Future Research Directions: Recommendations for Paleontological studies in Brazil
As paleontological studies in Brazil continue to uncover groundbreaking discoveries, particularly with the recent identification of new Triassic archosauriforms, there exists a compelling need for enhanced research methodologies to further our understanding of these ancient ecosystems. Future investigations should focus on multi-disciplinary approaches,integrating geology,climatology,and biology to construct a more complete picture of the environmental conditions that influenced archosauriform evolution. additionally, the implementation of advanced imaging technologies, such as 3D scanning and CT imaging, can provide deeper insights into the morphology and functional adaptations of fossil specimens, enabling researchers to draw more informed conclusions about their ecological roles.
Furthermore,fostering collaborations between Brazilian institutions and international research communities can facilitate resource sharing and knowledge exchange.emphasizing fieldwork in under-explored regions of Brazil, such as the Paraná Basin and the São Francisco Basin, may yield new fossil discoveries that enhance our understanding of archosauriform diversity and distribution. Establishing a centralized database for paleontological findings across Brazil could also streamline research efforts, ensuring that data is accessible to the global scientific community. focusing on these strategic directions will pave the way for innovative discoveries and broaden our understanding of Brazil’s rich paleontological heritage.
Wrapping Up
the discovery of this new species of Triassic archosauriform in Brazil marks a significant advancement in our understanding of prehistoric life during the Triassic period.As researchers continue to unearth fossils and analyze their implications, we gain valuable insights into the evolutionary pathways that led to the diverse array of reptiles and birds we see today. This finding not only enriches the fossil record but also emphasizes the importance of ongoing paleontological research in uncovering the mysteries of our planet’s distant past. As scientists further investigate this remarkable specimen, we can anticipate more revelations that could reshape our comprehension of the early archosauriform lineage and its adaptation to prehistoric ecosystems. The implications of this discovery are vast, offering a fresh perspective on the dynamic world of ancient life and inviting further exploration in one of the richest fossil beds on the planet.



