In a rapidly evolving global economic landscape, the escalating trade tensions between the United States and China have taken a prominent turn as Beijing has unveiled a series of retaliatory measures in response to the ongoing tariffs implemented during Donald TrumpŌĆÖs presidency. The latest developments reflect not only the deep-seated complexities of international trade but also the far-reaching implications for global markets, supply chains, and diplomatic relations. As both economic powerhouses brace for a protracted rivalry, the Financial Times delves into China’s strategic counteroffensive in this unprecedented trade conflict, analyzing the motivations behind its actions and the potential ramifications for businesses and consumers alike. With uncertainty looming large, this article aims to provide an in-depth examination of the current state of affairs, shedding light on how both nations are navigating this high-stakes battleground that is reshaping the future of global commerce.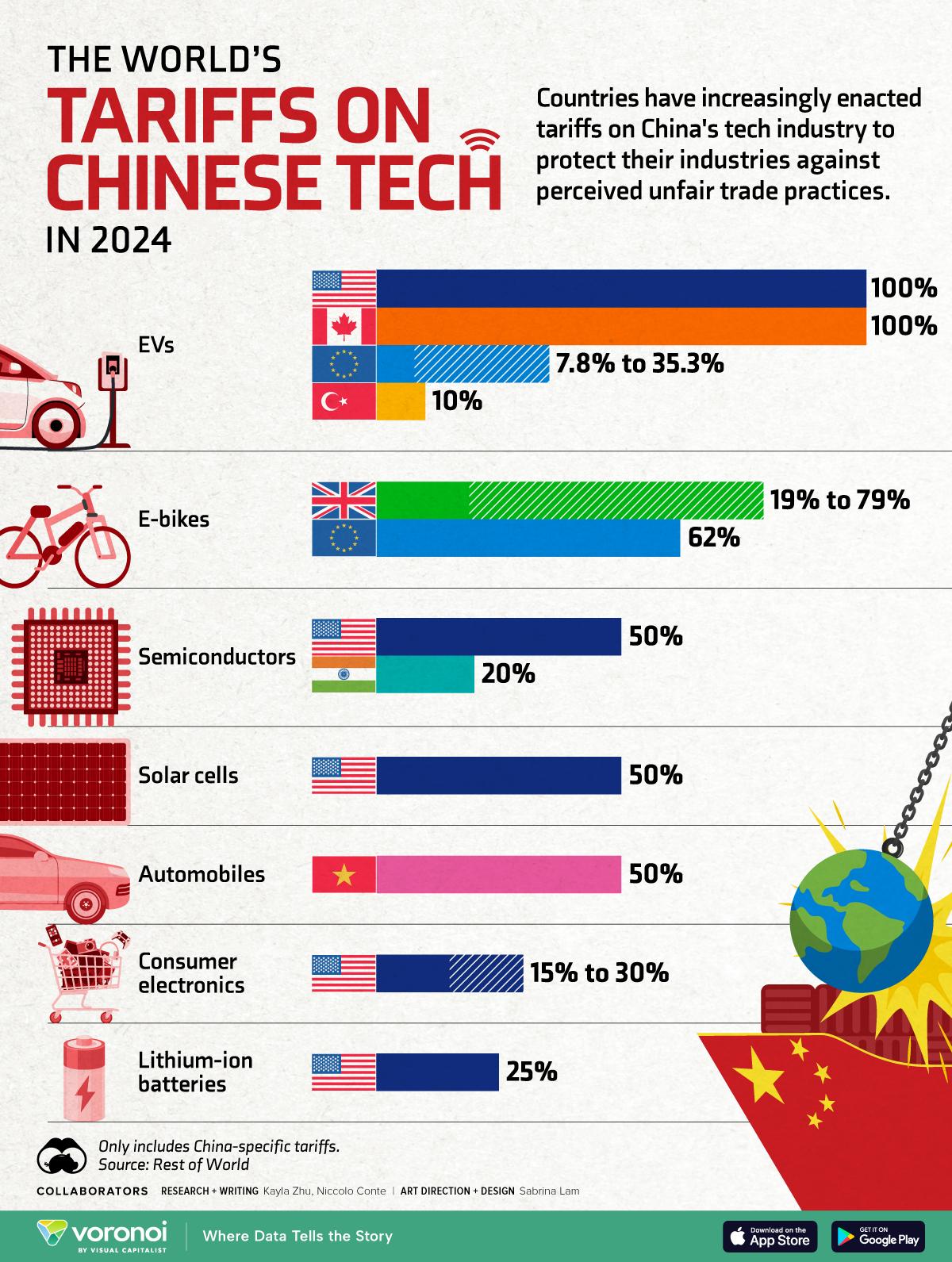
Chinas Strategic Response to U.S. tariffs and Its Impact on Global Trade
In response to increasing tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, China has demonstrated a strategy of both direct and indirect countermeasures aimed at protecting its economic interests. Beijing’s immediate reaction involved implementing retaliatory tariffs on a range of U.S. goods, effectively targeting industries that are politically sensitive in the U.S. These measures not only aim to safeguard critical sectors but also signal a robust opposition to perceived economic aggression.Key products affected include:
- Agricultural Goods: Soybeans, pork, and dairy products
- Manufactured Goods: Automobiles and electronics
- Luxury Items: Wine and handbags
Moreover, China has shifted its focus towards diversifying its trade partnerships to mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs. This includes strengthening ties with countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative and exploring opportunities within regional trade agreements such as RCEP (Regional Thorough Economic Partnership). Consequently, the impact on global trade dynamics is profound, leading to a reconfiguration of supply chains and fostering an habitat of uncertainty among international businesses. The following table outlines the estimated shifts in trade volumes attributed to this strategic pivot:
| region | Change in Trade Volume (%) |
|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | 15% |
| Europe | 10% |
| South America | 5% |

Analyzing the Economic Fallout: Industries Most Affected by the Trade War
The trade war between the United States and China has sent shockwaves through various sectors of the economy, revealing notable vulnerabilities among key industries. The agricultural, technology, and manufacturing sectors have been particularly hard hit as tariffs increase costs and disrupt global supply chains. Farmers have faced reduced access to the Chinese market, leading to a decline in soybean and pork exports, while technology firms grapple with escalated tariffs on components crucial to production. This environment has compelled many businesses to reevaluate their pricing strategies and explore choice markets to mitigate losses.
Along with agriculture and technology, the manufacturing sector has seen profound effects, particularly in industries reliant on raw materials and components supplied from China. Automotive, steel, and textiles have all reported increased operational costs due to higher tariffs, prompting some companies to consider relocating production to countries with more favorable trade agreements. To illustrate the impact, consider the following table highlighting some of the most affected industries, along with their primary challenges:
| Industry | Key challenges |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Loss of export markets, decreased crop prices |
| Technology | Increased component costs, supply chain disruptions |
| Manufacturing | Higher production costs, reconsideration of sourcing |
| Automotive | Increased tariffs on parts, potential price hikes for consumers |

Diplomatic Maneuvering: How China is Strengthening Alliances Amidst Tensions
In a landscape fraught with geopolitical tensions, China has proactively engaged in a series of diplomatic initiatives aimed at reinforcing its global alliances. The nation has sought to strengthen ties with key countries through a multifaceted approach that includes trade partnerships, cultural exchanges, and participation in international organizations. By aligning itself with nations facing similar economic pressures or geopolitical challenges,China is building a robust coalition that could counteract Western influence and facilitate a more favorable international environment.
Notably, China has diversified its diplomatic efforts by:
- Enhancing economic ties: Expanding trade agreements and investment projects, particularly in regions such as Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Engaging in multilateral diplomacy: Actively participating in forums like the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, where it collaborates with countries like Russia and India.
- Cultural diplomacy: Promoting Chinese culture and soft power through educational programs and exchanges.
| Country | Key Partnership Focus |
|---|---|
| Russia | Military cooperation and energy deals |
| Pakistan | infrastructure investments under CPEC |
| Brazil | Agricultural trade and technology exchange |
This intertwined strategy of engagement not only bolsters China’s influence but also positions it as a counterbalance to the unilateral actions frequently enough employed by Western powers. As alliances strengthen, the implications for global trade dynamics become increasingly significant, making China’s diplomatic maneuvering a key element in the reshaping of international relations in the coming years.

Recommendations for Businesses: Navigating Supply Chain Challenges in a Polarized Market
As businesses navigate the complexities of a polarized market, it is indeed crucial to adopt a flexible and strategic approach to supply chain management. Companies should prioritize diversification of their suppliers to minimize risks associated with geopolitical tensions. This involves establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions,reducing reliance on any single source. In addition, organizations should invest in technology that enhances visibility across their supply chains, facilitating real-time insights into production, inventory levels, and potential disruptions. Tools such as supply chain management software and data analytics can empower businesses to make informed decisions quickly.
moreover,fostering collaboration with suppliers and partners can led to improved resilience. Businesses should consider forming alliances that promote information sharing,enabling stakeholders to anticipate challenges and respond effectively. Regularly assessing market trends and consumer preferences will also aid organizations in adapting to shifts while maintaining competitiveness. Lastly, establishing a robust risk management framework that accounts for political, economic, and environmental factors is essential in todayŌĆÖs volatile landscape.
In Conclusion
As the trade tensions escalate between the world’s two largest economies, China’s strategic response to Donald Trump’s tariffs underscores the intricate dynamics of global trade relations.Analysts predict that this tit-for-tat exchange will not only impact bilateral trade but also have far-reaching consequences for international markets and supply chains. with both nations digging in their heels, the potential for a protracted conflict remains high, prompting stakeholders across the globe to recalibrate their strategies. As we continue to monitor this unfolding story, it is imperative to consider the broader implications of these trade policies and their potential to reshape the economic landscape in the years to come. The path ahead may be fraught with uncertainty, but one thing is clear: the repercussions of this trade war will resonate far beyond the borders of China and the United States.