In‚Äč a significant advancement in international security dialog, French President‚Äč Emmanuel‚ĀĘ Macron has‚Äč signaled France’s willingness to engage in ‚Äćdiscussions regarding ‚Äćthe potential extension of ‚ÄĆits nuclear deterrence strategy. This statement,‚Äč reported by The New York Times, comes‚Ā£ amid escalating geopolitical tensions and evolving ‚Ā£security ‚ĀĘlandscapes in ‚ĀĘEurope and beyond. As ‚Äčglobal leaders grapple‚ÄĆ with ‚Ā§the implications‚Ā£ of nuclear strategy‚Äč in contemporary conflict,Macron’s ‚ÄĆremarks ‚Äčopen‚ĀĘ the floor for critical conversations about deterrence policy and ‚ÄĆits role in ensuring‚Ā£ national and international stability. The discussions ‚Äćcould pave the way for collaborative frameworks‚ÄĆ that address‚Äć contemporary security threats,‚Äć while also‚Ā§ emphasizing the responsibilities‚Äć of‚Ā£ nuclear-capable nations in an increasingly complex ‚ĀĘworld.
Frances‚ĀĘ Position‚Äć on Nuclear ‚ĀĘDeterrence ‚ĀĘand Global Security Dynamics
France’s ‚ĀĘapproach to‚Äč nuclear deterrence emphasizes the necessity of ‚ĀĘmaintaining ‚Äća ‚ÄĆstable and‚Äć secure environment‚ĀĘ while navigating the complexities of global ‚Ā§security dynamics.President‚ĀĘ Emmanuel‚Äć Macron has indicated that France is open to‚Ā£ discussions regarding the extension and adaptation‚ĀĘ of its ‚ĀĘnuclear capabilities. This potential shift highlights the country’s commitment to ‚ÄĆensuring that its deterrent remains relevant in a‚Äč changing geopolitical landscape, particularly in the face of‚Ā£ evolving threats from‚ÄĆ state and‚Äć non-state actors. Key‚ÄĆ points of ‚ÄĆFrance’s strategy include:
- modernization of‚Ā£ Forces: Continuous ‚Ā£updates to France’s nuclear‚Ā£ arsenal to address technological advancements‚ÄĆ and‚ÄĆ emerging challenges.
- Multilateral Engagement: Strengthening collaborations with NATO allies and European partners to promote collective‚Ā§ security.
- Deterrence Philosophy: ‚ÄčReinforcing nuclear deterrence as a means of preventing conflict and asserting national sovereignty.
The‚Äć implications of Macron’s willingness to ‚Ā£discuss nuclear deterrence extend beyond France, affecting global security frameworks‚ÄĆ and alliances. In this context, the French‚Äć government is advocating‚ĀĘ for‚Äć a ‚ÄĆdialogue ‚ĀĘthat encourages clarity and mutual understanding among ‚Ā£nuclear and non-nuclear states. Through‚Äć this engagement, ‚Ā£France aims‚ÄĆ to foster a responsible discourse around ‚Ā§nuclear‚Ā£ armament and disarmament, ultimately ‚Äčleading‚ÄĆ to enhanced stability. The following table illustrates some of the core elements ‚Ā£shaping France’s nuclear policy:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Deterrence Strategy | Anchored in the concept ‚ĀĘof credible retaliation against aggression. |
| Diplomatic Relations | Promotes arms‚Ā£ control agreements and negotiations ‚ĀĘwith other powers. |
| Innovation | Investments in new‚ÄĆ technologies ‚Äćfor effective deterrence capability. |

Macrons Call‚ĀĘ for Diplomatic Dialogue‚Äć on‚Äć Nuclear Strategy
In a significant‚Äč shift in France’s stance on nuclear deterrence, President Macron has expressed openness to *establishing diplomatic dialogues* regarding the ‚Ā§extension ‚Äćof‚Äč the ‚Ā£nation’s nuclear‚Äč strategy.This marks ‚ÄĆa pivotal moment as‚Äć it ‚ÄĆcould pave the‚Ā£ way for‚Äč renewed international discussions concerning nuclear capabilities and security measures among western‚Äć allies.‚Äč Macron emphasized the‚ÄĆ importance of clear interaction, pointing out that engaging‚Äč with ‚Äčglobal ‚Ā§partners on these ‚Ā§matters is crucial for fostering an environment of stability and mutual‚Ā£ understanding.‚ÄĆ This ‚Ā£dialogue may‚Ā£ also act as a catalyst for addressing public‚ĀĘ concerns about nuclear arsenals in a rapidly changing geopolitical landscape.
French‚Äć officials‚Ā§ have indicated ‚Äćthat the proposed ‚Äćdiscussions would focus on several key areas:
- Strategic Stability: ‚Äć Assessing and ‚ÄĆenhancing ‚Äčcollective security frameworks.
- Nuclear Modernization: Evaluating advancements in nuclear ‚Äčtechnologies and‚Ā£ their implications.
- Arms Control: Exploring opportunities ‚Äčfor‚ĀĘ negotiations on nuclear‚Ā§ disarmament‚Ā§ and non-proliferation.
the‚Ā§ prospect of‚Ā£ these talks‚Ā£ fosters‚Ā£ hope for ‚ÄĆa‚ÄĆ more cooperative approach to global security, suggesting that dialogue rather than isolation could define future nuclear policies.Moreover, by advocating for‚ĀĘ *multilateral engagement*, Macron reinforces France‚Äôs commitment to playing‚Ā§ a pivotal role in shaping a safer international environment for all nations.

Implications of an Extended Deterrence‚Ā£ Policy for European Stability
The consideration of an extended deterrence policy by France, as indicated‚Ā£ by President ‚Ā§Macron’s openness to‚ÄĆ discussion, carries significant implications for‚Ā§ the stability‚ÄĆ of Europe. Extended‚Äć deterrence ‚Äć refers to‚ĀĘ the commitment to defend ‚ÄĆallies through nuclear capabilities, which can bolster ‚ĀĘcollective security‚Äć arrangements within the European landscape. This approach may enhance the defense posture against‚ĀĘ external threats,‚Ā§ particularly‚ĀĘ from nations‚Ā§ with ‚Ā§aggressive military ambitions. however, ‚Äčit may also‚ĀĘ provoke escalation‚Ā§ of tensions among adversaries, prompting a ‚ĀĘpotential arms ‚ĀĘrace that could‚Ā§ destabilize ‚ÄĆthe region further.
Moreover, the logical extension ‚Ā§of ‚ÄĆnuclear deterrence raises ‚Äćquestions ‚Ā£about trust ‚Ā§ among European nations, ‚ÄĆespecially within NATO. As countries evaluate their security needs‚Äć considering ‚ÄĆa more pronounced ‚ĀĘnuclear‚Ā§ stance, the dynamics of ‚Ā£defense collaboration might ‚Äćshift. A few key considerations include:
- Strategic Dependence: Nations‚Ā£ may become reliant on France’s nuclear shield, potentially ‚Äćundermining their own defense initiatives.
- Alliance ‚ÄćCohesion: Balancing the‚Äč interests‚Äč of various European states could strain relationships‚Ā£ within NATO.
- Public ‚ÄćPerception: The‚ÄĆ debate surrounding nuclear policy could‚Ā£ influence ‚ĀĘpublic opinion on defense strategies and military investments.
In analyzing ‚Ā£these implications, it’s ‚ĀĘevident‚Äč that the decision‚Ā£ to extend ‚Äćdeterrence must be evaluated not only on military terms ‚ĀĘbut also ‚Äćthrough ‚ĀĘthe lens of diplomatic ‚Äčrelations and the broader strategic landscape in europe.
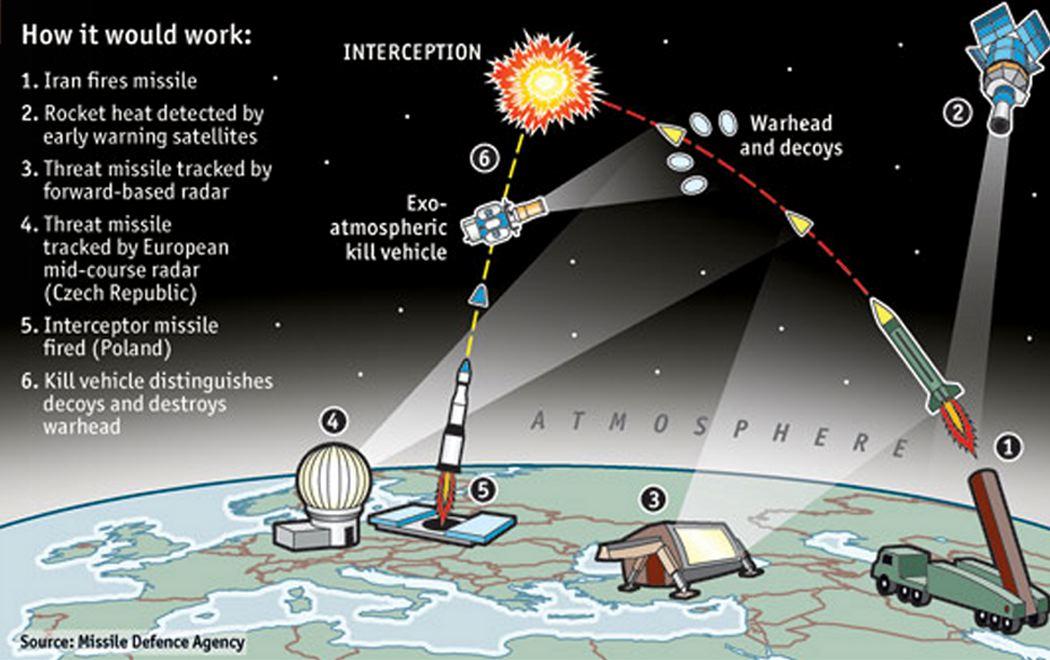
Engaging ‚Ā£allies: Strategies for Collaborative Nuclear Defense Initiatives
As ‚Ā§global security dynamics‚ĀĘ evolve, collaboration among‚Äč nuclear ‚Ā§powers is becoming‚ĀĘ increasingly vital. France’s recent openness to discuss‚Ā§ the extension of its nuclear deterrence umbrella highlights an urgent need‚Ā§ for a cohesive strategy among allies. France’s approach could serve‚Äč as a‚ĀĘ template for creating joint frameworks that address shared security concerns. Key strategies to foster these‚ĀĘ collaborative‚ĀĘ efforts include:
- Regular Diplomatic Engagements: Establishing consistent communication channels‚Äč among‚Äć nuclear states helps build trust and mutual understanding.
- joint Military Exercises: These initiatives bolster readiness‚Äć and improve interoperability among allied armed forces, showcasing a united ‚Ā£front.
- Shared ‚ĀĘTechnological‚Äć Development: Pooling resources ‚Äčfor research‚Äč into advanced defense technologies can enhance deterrent capabilities.
Furthermore, implementing ‚ÄĆa structured framework for cooperative‚Ā§ planning can ensure that all parties ‚Äćare aligned‚ĀĘ with ‚Ā£strategic objectives. Consideration should be ‚Äčgiven to forming ‚Äćbilateral‚Äć and‚ÄĆ multilateral committees that focus on nuclear‚Ā£ strategies and arms control. A simple‚Äć illustration of‚Äć possible ‚ĀĘmultilateral engagement mechanisms can be seen ‚Ā£in‚ÄĆ the table below:
| Engagement Mechanism | Involved‚Ā£ Parties | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Bilateral‚Äć Dialogues | France & UK | Strengthen‚ÄĆ deterrent strategies |
| Multilateral Summits | NATO Members | Enhance ‚ÄĆcollective defense measures |
| Joint‚Ā£ Research Initiatives | EU Nations | Develop new technologies |
Closing Remarks
President‚Äć Emmanuel Macron’s recent remarks regarding‚ÄĆ France’s openness ‚Ā£to discussing ‚Äčthe extension of its nuclear deterrence ‚Ā£underscore a significant moment‚Äč in the ongoing discourse ‚Ā£surrounding national security and global stability. As geopolitical tensions rise and the landscape of international relations evolves, France appears poised to play a‚Äč proactive role in‚Äć shaping the dialogue on nuclear strategy. With the potential ‚ÄĆimplications for both NATO allies and adversaries, the French ‚Ā§government’s ‚ĀĘstance invites further ‚Ā£examination of how nuclear ‚ĀĘdeterrence will factor into future diplomatic efforts and security ‚Ā§frameworks. As‚ĀĘ the global community‚Ā§ watches‚Ā£ closely, ‚Äćthe unfolding discussions ‚ĀĘwill ‚Äćlikely‚Ā§ influence ‚Äćnot only ‚ĀĘFrance’s defense policies ‚Ā§but‚Ā§ also the ‚ÄĆbroader dynamics ‚Ā§of nuclear policy in an increasingly complex world.




