As coffee lovers eagerly reach for their morning cup, many might potentially be surprised Ōüżto discover the rising price of their beloved brews. Behind the fluctuating costs of coffee lie complex dynamics rootedŌüó in agricultural Ōüżpractices, global trade, and environmental factors.At the heart of this coffee conundrum is Brazil,the world’s leading coffee producer,whose farms have become aŌĆī microcosm of the industry’s challenges and triumphs. In the article “Why is ŌüóYour Morning joe So Expensive? BrazilŌĆÖs CoffeeŌüŻ Farms Have the Answer,” The WashingtonŌüż Post explores howŌĆŗ Brazil’s uniqueŌüŻ climatic conditions, economic pressures, and labor practices contribute to the escalating prices of coffee beans. By delving into the intricacies of this vital industry, the piece sheds light on what coffee drinkers need to understand about the factors influencing their daily ritual and Ōüżthe future of theŌĆŗ coffee marketŌüŻ overall.
The Rising CostŌĆī of Coffee: Factors Driving Prices in the Global Market
The surge in coffee Ōüżprices can be attributed to aŌüż confluence of factors heavily influencedŌüó by ŌĆŹclimatic fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and economic instabilities. Brazil, as the worldŌĆÖs leading coffee producer, faces a unique set of challenges that impact itsŌĆŗ harvest. SomeŌüó key elements include:
- Climate Change: Increasing temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns are detrimental to coffee crops,leadingŌĆŹ to reduced yield and quality.
- Pests and Diseases: Renewed invasions of pests such as the ŌĆŗcoffee borer Ōüżbeetle and fungal diseases areŌüó wreaking havoc on plantations.
- labor Shortages: The pandemic has resulted in a important decline in available labor, affecting the harvesting process.
- Global Demand: A growing coffee culture worldwide, notably in markets like ŌĆīthe U.S. and Europe, intensifies competition for high-quality beans.
Additionally, economic factors are exacerbating theŌüż situation. The following outlines some of the crucial financial Ōüżinfluences:
| Factor | Impact on Prices |
|---|---|
| Currency Fluctuations | Changes in the Brazilian Real Ōüżcan make exports more expensive for international buyers. |
| Shipping Costs | Rising transportation expenses contribute to overall price increases for coffee globally. |
| Inflation Rates | Higher inflation not only affects production costs but alsoŌüó consumer prices in cafes and stores. |
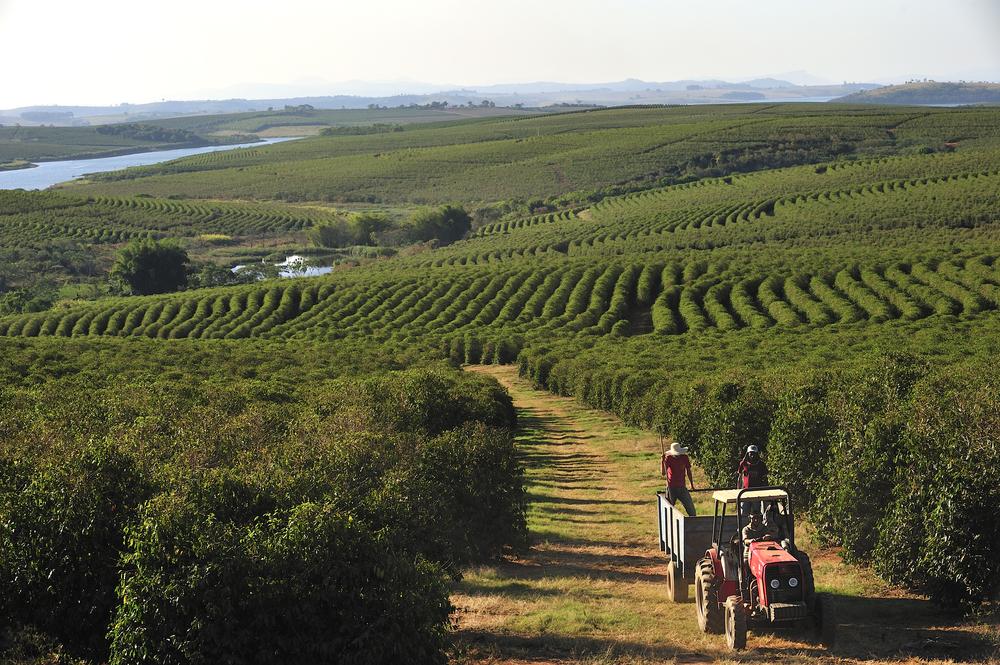

Brazils Key Role:Ōüó Understanding the Impact of Climate Change Ōüóon Coffee Production
Brazil, Ōüóas the world’s largest producer of coffee, plays a crucial role in the global coffee supplyŌüŻ chain. ŌĆīHowever, changing climate conditions are threatening the viability of coffee farming in the region. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation ŌüŻpatterns have led to increased vulnerability to pests and diseases, significantly impactingŌüŻ crop yields.According to experts, this has resulted in a significant decline in ŌĆŗArabica coffee production, the most sought-after variety, which isŌüŻ sensitive toŌüż variations in climate.
The implications of these changesŌüŻ are profound, affecting not only producers but also consumers worldwide, as ŌĆŹthe cost of coffee rises. Farmers face tough decisions about how to adapt their practices. Some strategies being explored include:
- Shifting cultivation practices to more sustainably farm coffee plants.
- Investing in drought-resistant crop varieties that can ŌĆŗwithstandŌüż harsher climatic conditions.
- Utilizing shade-grown coffee techniques to protect plants from excessive sun exposure.
As climate change continues to present challenges, the need for innovation in coffee farming practices becomes ever more critical.Below is a ŌüŻsummary of the factors influencing coffee production in Brazil:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Temperature Increase | Reduced yields and affected flavor profiles |
| Altered Rainfall Patterns | Increased risk of drought or flooding |
| Pests and Diseases | Higher incidence ŌĆŹleading to ŌüŻcrop loss |
| Global Demand | Strains local production and raises prices |

Labor Challenges: The Human ŌüóCost Behind Premium coffee Beans
In theŌüó quest for the perfect cup of coffee, ŌüŻconsumersŌüŻ often overlook the complex realities faced by those who cultivate and harvest these premium beans. The labor conditions on Brazil’s coffee farms starkly contrast with the elegance and allure of the final product. Many farmworkers endure grueling hours, often without fair wages, to ensure that ŌĆīthe coffee reaches our mugs. Their efforts are compounded by Ōüóenvironmental challenges, fluctuating market prices, and the ongoing threat of climate ŌüŻchange, all of which contribute to ŌĆŹthe rising costs of coffee. A look into the daily lives ofŌĆŗ these laborers reveals a concerning truth: the price of coffee reflects more than just quality; it encompasses aŌüó human element ŌĆīthat is integral to the industry.
While coffee lovers relishŌüż their morning brews, many are unaware of the struggles that accompany Ōüżhigh-demand production. Workers mayŌüŻ face:
- Excessive Work Hours: Extended shifts that exceed the legal limits in some regions.
- Low Compensation: ManyŌüż laborers earnŌĆŗ less than theŌüŻ minimum wage,struggling to meet basic needs.
- Lack of Benefits: Few benefits or protections, leaving workers vulnerable to exploitation.
The ripple effect of these labor challenges can lead to increased costs for consumers. As ethical sourcing becomes increasingly critically important, the high price tag of premium coffee may alsoŌüó serve as aŌĆŗ reminder to support fair labor practices. A growing number of companies are now focusing on sustainable ŌĆŹsourcing and providingŌĆŹ fair wages to ŌüŻensure that the complexities of the coffee supply chain do not come at the expense ofŌĆŹ those who work within it.
Navigating the Price hike: Strategies for Consumers to Adapt to HigherŌĆī Coffee Costs
As coffee prices continue Ōüżto rise, consumers are feeling the pinch during theirŌüó daily caffeine rituals. adapting toŌüó these higher costs requiresŌĆŹ strategic adjustments in purchasing habits. consider buying in bulk from ŌĆŗlocal roasters or specialty stores, where you may find discounts on larger quantities. Additionally, exploring off-brand or lesser-known coffee varieties can provide quality brews at lower prices. Engaging in community coffee-buying groups can also ŌĆŗreduce costsŌüŻ while ŌüŻfostering connections with fellow enthusiasts.
Another effective approach to manage your coffeeŌüŻ budget is to analyze yourŌĆŹ brewingŌüŻ methods. Utilizing manual brewing techniquesŌĆösuch as pour-over or French pressŌĆöcan enhanceŌüż your coffee experience while using fewer beans per cup. Furthermore, reducing coffee shop visits and optingŌüó for home-brewed alternatives allows you to enjoy your favorite drinks without the added premium. Below is a comparison of Ōüżpotential savings from varied coffee choices:
| Coffee Type | average Cost per Cup | Potential Savings perŌĆī Month |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Brand | $5.00 | $150 (assuming daily purchase) |
| Local Roaster | $3.50 | $105 (assuming daily purchase) |
| Homemade Brew | $1.50 | $45 (assuming daily purchase) |
Final Thoughts
the rising cost of your morningŌüŻ cup of coffee can beŌĆŹ traced back to ŌüŻa complex interplay of environmental, economic, and social factors rooted deep within BrazilŌĆÖs coffee-producing regions. From Ōüóclimate change impacts to labor shortages and supply chain ŌĆŹdisruptions, theŌĆī challenges ŌüżfacingŌĆŗ coffee farmers are significant and multifaceted.ŌĆī As consumers, understanding these nuances not only provides insight into why prices haveŌüż surged, but also emphasizesŌüŻ the importance of sustainable practices and Ōüóethical sourcingŌĆŗ in the coffee industry. As we savor our daily brew, weŌüż are reminded of the global tapestry that contributes to our favorite beverageŌĆöone that deserves our respect andŌüŻ attention.



