Introduction: Argentina is Dry – WNAX
As South america grapples with the impacts of climate change, Argentina stands at a pivotal crossroads, facing a challenging reality marked by increasing aridity. with recent reports highlighting record-low precipitation levels,the country’s agricultural heartland is under important strain,threatening not only local economies but also food security across the region.This article delves into the multifaceted implications of Argentina’s drying landscape, examining the environmental, economic, and social factors at play. From the vast Pampas to the arid regions of Patagonia, we explore how communities are adapting to this new normal and what it means for the future of a nation historically characterized by its lush resources. As we navigate through these changes, it becomes imperative to consider both the immediate challenges and the long-term strategies needed to sustain Argentina’s agricultural heritage in an increasingly unpredictable climate.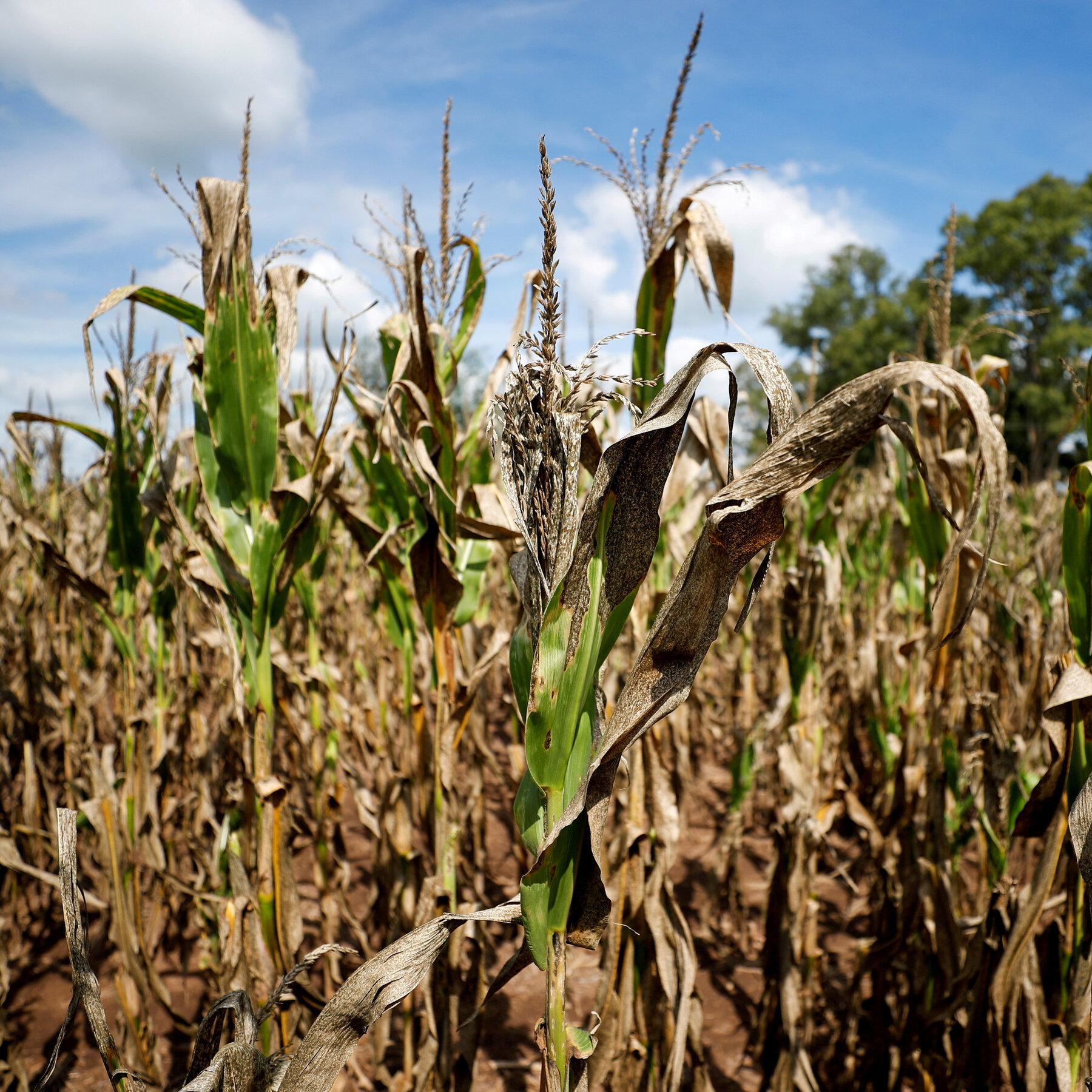
Argentina Faces Severe Drought Challenges Impacting Agriculture and Economy
Argentina is grappling with an unprecedented drought, considerably affecting its agricultural outputs and threatening the stability of its economy.Farmers across the country are reporting alarming declines in the yields of key crops, such as soybeans, corn, and wheat, which are essential not only for domestic consumption but also for export.The critical nature of this drought is not just a natural disaster; it is a complex crisis interwoven with economic implications that could have lingering effects well into the future. The following factors highlight the severity of the situation:
- Decreased Crop Yield: Many regions have seen crop production drop by as much as 40% this season.
- Financial Stress: Farmers face mounting debts due to rising costs and diminished income.
- Export Challenges: Argentina is at risk of losing its position in the global agricultural market, as key competitors may capitalize on its reduced output.
The implications extend beyond just immediate agricultural outcomes. the decline in crop yields is projected to have a cascading effect on the national economy,leading to potential job losses in rural areas and increased food prices for consumers. As the Argentine government scrambles to find solutions, including potential aid for affected farmers, the need for lasting water management practices is more pressing than ever. An analysis of economic indicators showcases the stark reality of this drought:
| Indicator | Current Status | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Crop Yield Reduction | 40% decrease | Economic downturn |
| Job loss Potential | Thousands at risk | Increased unemployment |
| Food Price Inflation | 15% increase | higher costs for consumers |

Expert Insights on the implications of Reduced Water Resources in Argentina
As Argentina faces unprecedented drought,the implications of reduced water resources are reshaping economic landscapes and social dynamics. experts warn of the profound effects on agricultural productivity, which is pivotal for the country’s economy. Key sectors are likely to experience:
- Decline in Crop Yields: Essential crops such as soybeans and corn may face severe reductions, threatening both local food supplies and export revenues.
- Increased costs: Farmers may need to invest more in irrigation technology, raising production costs and squeezing margins.
- Job Losses: As agriculture struggles, potential job losses in rural areas could lead to increased migration to urban centers, straining infrastructure and resources.
Moreover, the social implications are equally significant. Water scarcity not only threatens livelihoods but can also exacerbate existing inequalities. Vulnerable communities,often in the most affected areas,may struggle to access clean water for basic needs,leading to:
- Health Risks: Limited water availability can heighten risks of waterborne diseases,as access to sanitation becomes compromised.
- Conflict Over Resources: Competition for dwindling water supplies can spark tensions between agricultural and urban areas.
- Policy Challenges: Governments will need to implement innovative strategies to manage water supply and distribution effectively amidst growing pressure.
| Impact Area | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Reduced crop yields, increased production costs |
| Employment | Job losses in farming, urban migration |
| Health | Increased disease risk, limited sanitation |
| Societal Stability | Tensions over resources, policy challenges |

Strategic Recommendations for Adapting Agricultural Practices Amidst Drought
To ensure resilience in agricultural production during prolonged dry spells, farmers should consider a series of strategic adaptations. One of the primary approaches is the adoption of drought-resistant crop varieties,which are engineered to endure harsh environmental conditions while maintaining yield. Additionally, implementing crop rotation can diversify soil health and make it more resilient against drought conditions. Other strategies may include:
- Soil Moisture management: Utilize mulching techniques to reduce evaporation and retain soil moisture.
- Precision Irrigation: Introduce drip or sprinkler systems that minimize water waste and target irrigation to where it’s most needed.
- Conservation Tillage: Reduce tillage to enhance soil structure and moisture retention.
Moreover, educating farmers about whether forecasting technologies can bolster their proactive measures against drought. Collaborations with agricultural extension services will provide valuable support and resources to ensure effective implementation. A table below outlines potential interventions and their expected benefits:
| Intervention | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drought-Resistant Seed Varieties | Higher resilience and improved yield |
| Precision Irrigation Techniques | Efficient water usage and reduced waste |
| Crop Rotation | Improved soil health and pest management |
| Moisture Retention Practices | Enhanced soil moisture for better crop longevity |

Community Response and Resilience: How Argentinians Are Coping with Dry Conditions
In the face of relentless dry conditions,communities across Argentina have come together,showcasing remarkable solidarity and ingenuity. Local farmers have banded together to share resources,implement water conservation techniques,and distribute crops to those in need. Many have adopted drought-resistant crops, which not only ensures food security but also fosters a sense of community resilience. Public awareness campaigns emphasize the importance of sustainable practices, reminding residents of simple yet effective measures like:
- Recycling water from household activities
- Using drip irrigation in gardens
- Participating in local reforestation efforts
Moreover, community organizations have been pivotal in extending support. They provide emergency relief and support networks to assist with the strains brought on by the dry spell. Local governments are also stepping up, rolling out initiatives to equip towns with rainwater harvesting systems. Many towns have created resource hubs where residents can access data and support related to drought management. Collaborative efforts are critical, with volunteers actively participating in workshops to educate about climate adaptation strategies. This concerted approach not only aims to combat the immediate impact of drought but also reinforces the social fabric of these communities.
Future Outlook
the emerging narrative of “Argentina is Dry,” as highlighted by WNAX, underscores a crucial environmental and socio-economic challenge facing the region. The persistent drought conditions not only threaten the agricultural backbone of the country but also impact local communities and global markets that rely on Argentine exports. As climatological patterns shift and water resources become increasingly scarce, concerted efforts towards sustainable water management and agricultural innovation will be vital to mitigate the effects of this pressing crisis.Stakeholders across the board—from policymakers to farmers—must collaborate to address these challenges and foster resilience in the face of an uncertain climate future. Only through awareness and action can Argentina hope to navigate this dry spell and secure a sustainable path forward.