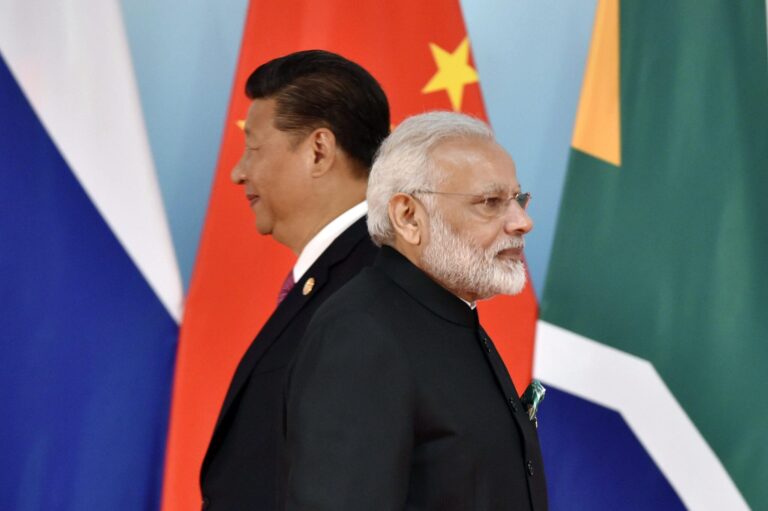
As tensions continue to simmer ‚ĀĘalong the‚Äć India-China border, the relationship between ‚Äćthe two neighboring giants remains one‚Ā£ of the ‚Äčmost complex and vital dynamics in asia.In‚Ā£ recent years, territorial disputes and military skirmishes have marred an otherwise historic partnership, challenging diplomatic ‚Ā£efforts and regional‚Ā£ stability.However,amid this backdrop ‚Ā£of ‚Ā§uncertainty,Indian Prime Minister ‚ÄćNarendra Modi is cautiously optimistic about the‚ĀĘ potential‚Ā§ for a thaw ‚ÄĆin‚ÄĆ relations. This article ‚Äčexamines Modi’s diplomatic approach‚Äć and‚Äč the broader geopolitical context that‚Äč shapes‚Ā£ India-China interactions, ‚Äćassessing the prospects for ‚ĀĘcooperation in ‚Ā§a rapidly evolving international ‚ÄĆlandscape. By exploring the implications of modi’s‚ÄĆ initiatives and‚Äć the challenges‚ĀĘ that lie ahead,‚Ā§ we aim to provide‚ĀĘ a complete‚Ā§ understanding of how‚Ā£ both nations might ‚ĀĘnavigate‚Äć their turbulent‚Ā§ ties in pursuit of mutual interests and‚Äč regional ‚Äčharmony.
The ‚Ā§Historical Context of India-China relations‚Äč and ‚ĀĘCurrent Tensions
The longstanding history of India-China relations has‚ÄĆ been shaped by‚ÄĆ a complex interplay of cultural exchanges, economic interactions, and geopolitical rivalries. historically,‚Ā§ India‚ĀĘ and ‚Ā§China have shared deep-rooted‚Ā§ cultural ‚Äčlinks, dating back to ancient times when ‚ÄćBuddhism spread‚Ā£ from ‚Ā£India to China. However,the relationship‚Äč has‚ÄĆ been fraught‚Äč with tensions,particularly since the Sino-Indian ‚ÄćWar of 1962,which highlighted territorial disputes along the Himalayan borders. ‚ĀĘThese disputes have ‚Äčnot‚ÄĆ only persisted but have also intensified, influenced ‚Äčby factors such as national‚ÄĆ identity, ‚Äćeconomic competition, and strategic alliances. The post-Cold ‚ÄĆWar era saw both nations ‚ĀĘnavigating their paths with an ‚Ā§eye on regional and global influence,‚ÄĆ yet ‚Äčthe unresolved ‚Äčissues ‚Ā§foster ‚Äčan underlying rivalry ‚Ā§that complicates diplomatic efforts.
In recent years, ‚Äčthe geopolitical landscape has‚Ā§ shifted dramatically, characterized by China’s‚Ā£ assertive policies in the‚Ā£ South China Sea and India‚Äôs growing‚ĀĘ military partnerships with Western nations. As India seeks to‚Ā§ solidify its standing as ‚Ā£a regional power, the stakes have risen substantially. with both‚Ā£ countries experiencing rapid‚Äć economic growth, their aspirations conflict, leading to strategic competition. ‚ÄčMoreover, the‚Äč rising nationalism within both nations adds another layer of complexity to their interactions.Recent skirmishes along the Line ‚Ā£of‚ĀĘ Actual Control ‚Ā§(LAC) have reignited tensions, ‚ÄĆdrawing international attention ‚Äčand‚Ā£ complicating ‚Äćdiplomatic channels.‚Äć To understand‚ÄĆ the‚Ā§ future of India-China relations,‚Ā£ it is vital to‚Äč recognize how these ‚Ā§historical‚Ā§ grievances and contemporary‚Äć challenges interact, ‚Ā§influencing‚Äć the possibility of a‚Ā§ diplomatic thaw in a ‚Ā§rapidly changing‚Ā§ geopolitical habitat.
Modi’s Diplomatic Strategy: ‚ĀĘBalancing ‚ÄćCooperation and ‚Ā£Competition
In recent years, Prime Minister Narendra Modi has‚Äć pursued a diplomatic strategy aimed at navigating‚Äć the complex landscape‚Äć of India-china relations, ‚Ā£characterized by both cooperation and‚ĀĘ competition. Recognizing‚Äć the significance of ‚Äčstable ties with China, Modi‚ĀĘ has engaged ‚ĀĘin multiple‚Ā£ dialogues‚Ā£ to address contentious issues and ‚ÄĆbolster‚Äč economic collaboration. ‚ÄĆThis approach is ‚Äćfurther underscored by ‚ÄćIndia’s participation in regional forums such‚ÄĆ as the Shanghai cooperation‚ÄĆ Association (SCO) and the ‚Ā£BRICS bloc, which ‚Ā£facilitate multilateral engagement‚Ā£ while allowing ‚ĀĘIndia to assert its interests. Key elements of this strategy include:
- Economic Partnerships: Enhancing‚ĀĘ trade and investment ties to ‚Äćbenefit both nations.
- Border ‚ÄćStability: Engaging in dialogues to‚ÄĆ resolve border ‚ĀĘdisputes and prevent military skirmishes.
- Climate‚Äč Change‚ÄĆ Cooperation: Working together on environmental initiatives, showcasing shared global‚ĀĘ responsibilities.
However, Modi’s diplomatic balancing ‚Ā§act ‚Ā§also‚Äć entails addressing China’s‚ĀĘ assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region, where China‚Äôs expansionist policies ‚Ā§often clash with India‚Äôs strategic interests. The Modi‚ĀĘ governance has focused ‚ÄĆon strengthening alliances with other regional powers, ‚ĀĘsuch as‚ĀĘ the United States, Japan, ‚ÄĆand Australia,‚Ā§ to counterbalance China’s influence. This‚ĀĘ includes:
| Strategic‚Äć Partner | Key Focus Area |
|---|---|
| United ‚ÄćStates | Defense Collaboration |
| Japan | Infrastructure investment |
| Australia | Maritime Security |
Challenges Ahead:‚ÄĆ Border Disputes‚Äć and Economic rivalries
The complex relationship between India and china is ‚Ā§marred by enduring border ‚Ā§disputes and escalating ‚Äčeconomic rivalries. The Line of Actual Control (LAC) remains a‚ÄĆ flashpoint, with skirmishes ‚Ā§and standoffs that flare up ‚Äćdespite ‚Äćdiplomatic efforts to establish a more‚Äč stable framework‚Ā§ for ‚Ā£cooperation. As both nations prioritize‚ÄĆ territorial integrity, ‚ÄĆthe challenge lies in addressing historical grievances while preventing conflicts that ‚ÄĆcould spiral‚Äč into larger confrontations.Tensions along the border include:
- Incursions by military personnel from either side.
- Infrastructure ‚ÄĆdevelopments in ‚ĀĘdisputed regions.
- Lack of effective interaction channels ‚ĀĘduring crises.
beyond territorial ‚Ā£challenges, economic competition‚Ā£ further ‚ÄĆcomplicates bilateral ‚Ā§relations. Both‚Äć countries are ‚Ā£vying ‚Äćfor ‚Äčleadership in‚Äč Asia, ‚ÄĆleading to‚ĀĘ friction in trade and investment.‚Ā£ Initiatives‚Ā£ like China‚Äôs Belt and Road initiative clash with‚Äć India‚Äôs vision‚Ā£ for‚ÄĆ regional connectivity, creating a battleground for influence. Key economic points of‚Äč contention include:
| Issues | India’s Stance | China’s Position |
|---|---|---|
| Trade Balance | Deficit reduction efforts | Focus ‚Ā§on increasing exports |
| Investment‚ĀĘ Policies | Encouraging FDI ‚Äčfrom varied‚Ā§ sources | Dominance in‚ĀĘ regional investments |
| Technological Competition | Promoting Make ‚Äćin India | Advancing tech exports |
Pathways to Peace: Recommendations‚Äč for Sustainable‚Äć Engagement
In navigating ‚Äćthe complexities of‚Ā£ India-China relations, both‚Ā§ nations stand at a pivotal crossroad where dialog and diplomacy can ‚Äćpave the way for lasting ‚Äčpeace and stability. ‚Ā§A multi-faceted approach that incorporates cultural‚Äć exchanges, economic collaborations, and ‚Ā§ people-to-people interactions can play ‚Ā§a‚Ā§ crucial‚Ā§ role in‚Äć bridging the current ‚Äčgaps. Initiatives aimed at fostering‚Ā£ understanding between diverse communities will reinforce the message that cooperation yields benefits far‚Ā§ exceeding‚Äč the costs of conflict. such engagement‚Äč not only nurtures goodwill‚ÄĆ but also‚Äć cultivates ‚Äća collective identity that transcends nationalistic fervor.
Additionally, establishing mechanisms for conflict resolution can facilitate constructive engagement and ‚ÄĆdiminish the potential for‚Äć confrontation. Countries must consider the following strategies:
- Regular‚ÄĆ high-level ‚Ā§meetings: To‚Äč ensure ongoing dialogue, ‚ĀĘengaging leaders regularly can help address emerging ‚ĀĘtensions‚ĀĘ before they escalate.
- joint economic‚ĀĘ projects: Collaborative ventures in ‚Ā£trade‚Ā£ and infrastructure can build interdependencies that discourage‚Ā§ aggression.
- Track II diplomacy: Involving non-governmental ‚Äčactors and civil societies can provide choice viewpoints and facilitate ‚Äćdialogue in a less formal setting.
To‚ĀĘ Wrap It ‚ÄćUp
As geopolitical tensions continue to shape‚Ā§ the‚Äč landscape‚ÄĆ of ‚Ā§international relations, the‚ÄĆ dynamics between India ‚Äćand China remain critical ‚Äčto regional stability and global peace. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent diplomatic overtures signal a potential thaw in ‚Äčwhat has been ‚Äča historically fraught‚Ā§ relationship. However, the path forward ‚Ā£is laden with‚ĀĘ challenges,‚Ā§ from border disputes to economic competition and ‚Ā§strategic alignments. ‚Ā£
As both‚Äć nations navigate these turbulent waters, the world watches closely, recognizing that the outcomes of India-China relations‚Äč could have‚ĀĘ far-reaching ‚Äćimplications not only‚Äć for ‚Ā§Asia‚Äč but ‚ÄĆfor the entire global order.‚ĀĘ Whether Modi’s hopes‚Äć for a renewed partnership can ‚ĀĘovercome the legacy of mistrust remains to be seen. Looking ahead, the ‚Äčcommitment‚Ā£ to dialogue, mutual respect, and collaborative solutions will be ‚ÄĆvital in reshaping these pivotal ties, offering a glimpse of what ‚Ā£may be possible in the intricate ‚ĀĘweb of international geopolitics.