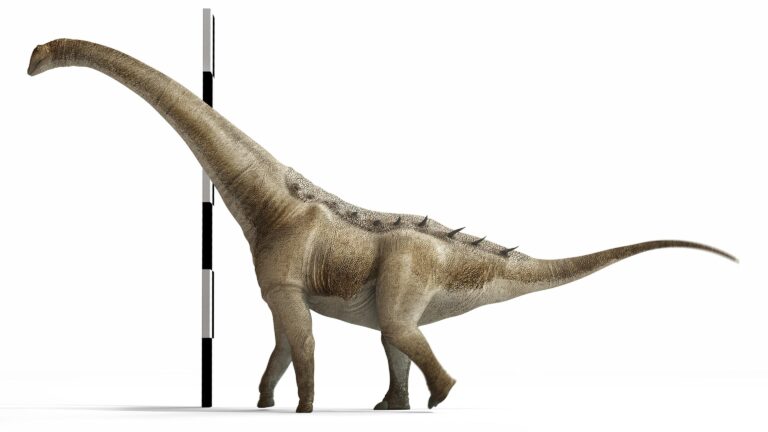
In a remarkable discovery that adds ‚Äćto the ever-growing catalog of prehistoric life, paleontologists have uncovered a new species‚Äč of titanosaur in Argentina, a colossal dinosaur measuring an remarkable ‚ĀĘ22 feet in length.‚Ā§ This find‚Äć not ‚Ā£onyl sheds light on the diverse fauna of the Late Cretaceous period ‚Ā£but also highlights‚ĀĘ the rich paleontological heritage of South America.‚ÄĆ As researchers sift through the geological layers of Argentina’s fossil-rich landscapes, they ‚Ā§continue to unveil the secrets of these splendid creatures that once roamed the Earth. The ‚Ā£recent discovery promises to ‚Äčenhance‚Äć our ‚Äčunderstanding of titanosaurs, a group known for their‚ĀĘ massive size and long necks, and invites‚Äč further‚ÄĆ exploration into ‚Ā£their evolutionary meaning. This article delves into the details of the find,‚Ā£ the implications for our understanding of dinosaur ‚Ā§diversity, and what this titanosaur reveals about life in the‚Ā£ distant past.
New Titanosaur ‚ÄĆSpecies Uncovered in‚ĀĘ Argentina Enhances Understanding of‚ÄĆ Dinosaur Diversity
Recent discoveries in Argentina have unveiled a new species of titanosaur that measures an remarkable 22 feet in length,adding a compelling chapter to ‚Äćour understanding of these colossal creatures. Fossil evidence was uncovered‚Ā§ in ‚Ā£the Patagonia region, with paleontologists excitedly noting the distinct‚Äč features that set this titanosaur apart from‚Äć its relatives. initial examinations suggest that this‚Äć species may have ‚ĀĘhad unique adaptations ‚ÄĆthat enabled it to thrive in its specific habitat during the Late cretaceous period. The findings emphasize the rich biodiversity that‚ÄĆ existed‚ĀĘ among sauropods, a‚ÄĆ group that has always intrigued scientists due to their ‚ÄĆimpressive size and varied ecological niches.
As researchers continue to analyse the skeleton,they are especially focused on:
- Bone structure – which may offer insights into locomotion and feeding strategies
- Teeth morphology – that could indicate dietary preferences
- Growth patterns – which might reveal ‚Äćhow these giants adapted to their environment over time
This discovery not only highlights ‚ĀĘthe evolutionary diversity of titanosaurs‚ĀĘ but also prompts ‚Ā£further exploration of‚Äč other unexplored sites across South America. Collaborative efforts may yield‚Ā§ additional fossils, enriching our comprehension ‚ÄĆof how these majestic creatures interacted ‚Ā§with their ‚Ā§ecosystems and each other.
Physical Characteristics and Habitat Insights of the Newly Discovered Titanosaur
The recently unearthed titanosaur, measuring an impressive 22 feet ‚ÄĆin length, showcases remarkable physical‚ĀĘ characteristics that‚ĀĘ distinguish it as one of the more robust members of its lineage. Characterized by‚Äč a long neck and a massive, barrel-shaped body, this giant dinosaur likely had several adaptations for ‚Ā§efficient feeding and ‚ÄĆlocomotion in its ancient ecosystem. ‚ÄčPaleontologists have noted‚ĀĘ several striking features:
- Robust ‚Ā£Limbs: Thick, ‚Äćsturdy legs capable of supporting its substantial weight.
- Long Tail: A long, muscular tail‚Äč that may have been used for balance ‚Ā§or interaction.
- Wide Feet: ‚ĀĘBroad feet providing stability while traversing various terrains.
- Small Head: A proportionately small‚Äć head relative ‚ĀĘto its body size, adapted for grazing.
This ‚ĀĘtitanosaur ‚ĀĘwas primarily discovered in‚Ā§ the sedimentary rock layers of Argentina,an area‚Ā£ known for its rich dinosaur fossil sites. Analysis of the geological context indicates this‚Äć creature‚Äć thrived ‚ÄĆin a lush, temperate environment dotted with expansive forests and diverse plant life. The habitat likely included:
| Terrain Types | Flora |
|---|---|
| Floodplains | Ferns and Cycads |
| Wooded Areas | Conifer Trees |
| Grasslands | Flowering Plants |
Such diverse habitats would have provided an ample food supply, ‚Äčenabling this titanosaur to thrive. The ‚Äčdiscovery of this‚Ā£ ancient giant illustrates not‚Ā£ only the evolutionary ‚ÄĆadaptations of sauropods but ‚Ā§also the ecological dynamics at play during its time on Earth.
Implications for paleontological Research and Conservation Efforts
The ‚ÄĆdiscovery of a new‚Ā£ 22-foot-long titanosaur in Argentina not‚ÄĆ only sheds light on the rich ‚Ā£tapestry of prehistoric life but also‚ĀĘ opens new avenues for‚ÄĆ paleontological research. The fossil evidence will provide critical insights into the evolutionary biology of‚Ā§ sauropods, particularly their ‚Äčadaptations to environmental changes during the Late Cretaceous. Researchers ‚Äčcan now ‚Ā£explore various hypotheses regarding their growth‚Äć patterns, behavior, and ecological roles. This obliges the scientific community to revisit existing models of sauropod behavior, possibly leading to revised‚ĀĘ theories on their social‚Ā§ interactions and ‚Äćreproductive strategies.
Moreover, the implications for conservation efforts are profound. As climate change continues to threaten biodiversity, lessons learned from the past can inform ‚ÄĆcurrent ‚ÄĆconservation strategies. By understanding the adaptive ‚Ā£strategies of‚Äć giant dinosaurs, modern conservationists can identify what factors allow species to thrive or become extinct under changing conditions. This research can contribute‚Äč to ‚Ā§the development of better preservation techniques that respect‚Äć both the geological ‚ĀĘcontext‚ĀĘ of fossil findings and the ecological systems in which they are found. By synthesizing this new‚ÄĆ data, we‚Äć can‚Äć enhance our preservation efforts and ensure‚Ā£ that ‚Äćthese ‚Äčancient wonders are protected for‚Äč future generations.
Recommendations for Future Excavations and‚Äć Study of Titanosaur Fossils
The ‚ÄĆdiscovery of the new 22-foot-long‚Ā£ titanosaur opens exciting avenues for further excavations and research. Future efforts should focus on several key areas to enhance our ‚Ā§understanding‚ÄĆ of these majestic creatures:
- Site Expansion: Continue excavating surrounding areas ‚ĀĘto ‚Äčuncover additional specimens, which may provide insights into the biodiversity of the ecosystem.
- Comparative Analysis: Collaborate with international teams to compare findings with other ‚ÄĆknown titanosaur fossils, facilitating a broader understanding of species variations.
- Technological Integration: Employ advanced imaging and scanning technologies to analyze the fossilized remains without causing damage, revealing hidden anatomical features.
- Stratigraphic Studies: Conduct detailed geological surveys of the excavation ‚Ā£sites to‚Äć better interpret the environmental conditions‚Ā£ in which these titanosaur fossils were‚Äć formed.
Moreover, a focus on public engagement and education ‚ÄĆwill ‚Ā§be‚Ā£ critical in elevating interest and support for‚ÄĆ paleontological research. Establishing interactive exhibits and providing opportunities for citizen scientists to ‚Äčparticipate in fieldwork can foster a deeper connection to the past. The following initiatives may be‚ĀĘ beneficial:
| Community Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Fieldwork Days | Invite local communities to participate in excavation days, providing hands-on experience. |
| Educational Workshops | Conduct workshops‚Äć in schools to teach about paleontology ‚Ā£and the significance of titanosaurs. |
| Virtual Tours | Develop online content‚Äč showcasing discoveries‚Äč and the excavation process to reach a wider audience. |
Concluding Remarks
the discovery of this‚Äč remarkable 22-foot-long titanosaur ‚ÄĆin Argentina ‚Ā§not only adds to our understanding of these colossal creatures that once roamed the Earth but also underscores‚ĀĘ the‚ÄĆ continual revelations that paleontology offers. As researchers delve deeper into this prehistoric giant’s skeletal structure and‚ÄĆ ecological role, they are likely to uncover insights that could reshape‚ĀĘ our comprehension of dinosaur evolution and behavior. This finding highlights the ‚Äčimportance of ongoing‚ÄĆ fossil exploration and conservation efforts in Argentina, where the rich sedimentary layers continue to yield‚Ā§ exceptional specimens. As scientists piece together the evolutionary puzzle of the titanosaur, we are reminded that the story of life on ‚Ā£Earth‚ÄĆ is still unfolding, and each new discovery serves as a testament to the wonders of our ‚ÄĆplanet‚Äôs ancient‚ÄĆ history. Stay tuned for ‚Ā§further updates as researchers continue to explore‚Äć the significance of this engaging find.